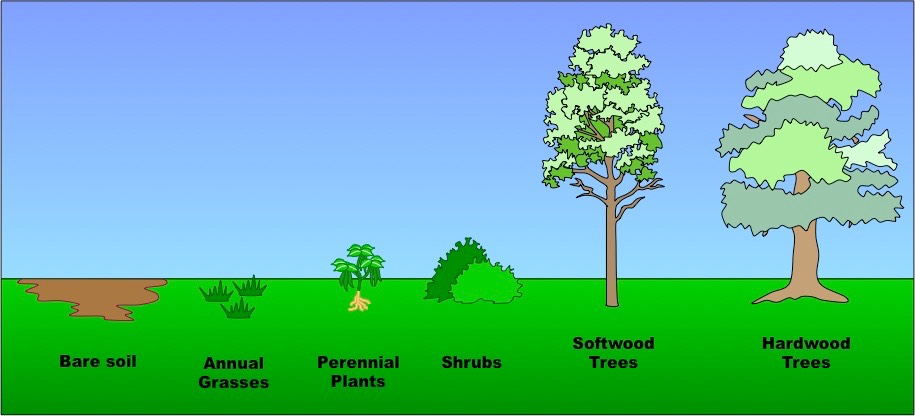
Pioneer species play a vital role in ecological succession, initiating the process of ecosystem development. These hardy organisms are the first to colonize barren or disrupted environments, paving the way for more complex plant and animal communities. Let’s delve into the fascinating world of pioneer species, examining their characteristics and exploring notable examples in nature.
hat are Pioneer Species?
Pioneer species are the resilient plants, fungi, and microorganisms that thrive in harsh or barren environments. Their ability to withstand tough conditions, such as poor soil quality or extreme climates, makes them the front-runners in colonizing disturbed areas.
Characteristics of Pioneer Species:
- Rapid Growth: Pioneer species are known for their quick establishment and growth, helping to stabilize the environment.
- High Reproductive Rates: They often have prolific reproduction methods, ensuring a swift colonization of the area.
- Adaptability: These species are adapted to survive in less-than-ideal conditions, showcasing resilience.
Examples of Pioneer Species:
- Lichens: Lichens, a symbiotic relationship between fungi and algae or cyanobacteria, are often the first colonizers on bare rock surfaces. Their ability to break down rock contributes to soil formation.
- Mosses: Mosses can thrive in nutrient-poor soils, and their ability to retain water aids in soil development. They’re common pioneers in disturbed areas.
- Pioneer Plants: Species like fireweed and aspen trees are known for colonizing areas after disturbances like wildfires. Fireweed, for instance, quickly covers burned landscapes, preparing the ground for other plants.
To Read More Example related Pioneer Species visit Here.
Role in Succession
Pioneer species play a crucial role in ecological succession by creating conditions suitable for more complex organisms. As they establish, they alter the environment, making it more habitable for other plant and animal species.
Human Impact:
Understanding pioneer species is essential for conservation efforts and land management. Human activities often disrupt ecosystems, and recognizing the role of pioneer species aids in restoration projects.
Conclusion:
Pioneer species, with their resilience and adaptability, set the stage for ecological succession. From the hardy lichens breaking down rocks to the rapid growth of plants like fireweed, these species showcase nature’s remarkable ability to reclaim and regenerate. Studying and appreciating these pioneers provide insights into the intricate processes of ecosystem development and environmental restoration.
Leave a comment